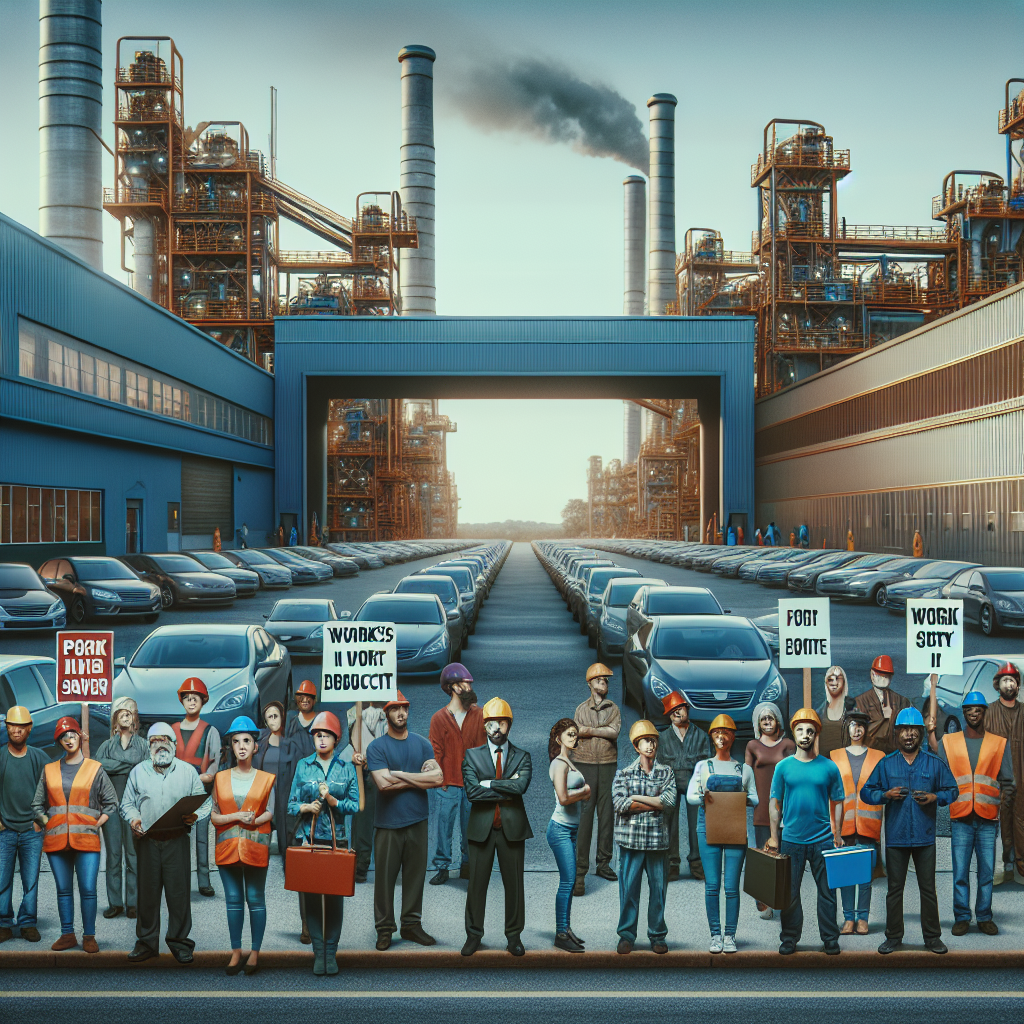
The automotive industry is experiencing significant disruptions as major manufacturers and suppliers grapple with labor disputes and economic pressures. From production halts at key facilities to substantial workforce reductions, the sector is undergoing a period of substantial transformation that affects both traditional and electric vehicle manufacturing operations.
German automotive supplier Bosch has announced plans for significant workforce reductions as part of its effort to maintain competitiveness in the evolving automotive market. The company will cut approximately 13,000 jobs across its operations, marking one of the largest restructuring efforts in the automotive supply sector [1].
Volkswagen is facing its own challenges, implementing cuts to electric vehicle production, particularly affecting the ID.4 model. The automaker is planning fresh plant shutdowns, indicating ongoing adjustments to market demands and production capabilities in the electric vehicle segment [2].
In South Korea, Kia's manufacturing operations have been significantly impacted by labor issues in its supply chain. A strike at a parts supplier has forced the automaker to halt production of both its new EV5 electric vehicle and the popular Sportage model [3].
These developments reflect broader industry challenges as automakers and suppliers navigate the transition to electric vehicles while managing labor relations and maintaining profitability. The simultaneous occurrence of production cuts, labor disputes, and workforce reductions suggests a period of significant adjustment throughout the global automotive supply chain.